The definitive guide to Whey Protein
In this guide you will find out all the details about Whey Protein.
What it is, what different types are available, their benefits and much more.
We tried to cover all the relevant topics about this supplement so that you can understand why it is so popular.
At the end, if you still have any questions, just use the comments area.
So let's get started.
What is Whey Protein?
It is a milk protein, more precisely from whey, and is obtained during the cheese manufacturing process.
Whey proteins make up approximately 20% of the protein content of animal milk, with the rest of the proteins being casein fractions (~80%).
The production of whey protein can be done through various filtration methods (microfiltration, ultrafiltration, etc.), depending on the desired protein content.
After being filtered, the protein is spray-dried to produce its desired powder format, after which it may undergo additional modifications by manufacturers, such as flavorings, colorings, etc.
It is a source of complete protein, which means that it contains all 9 essential amino acids, has a high biological value and a high concentration of BCAA's.
What are the different types of Whey Protein?
Whey Protein Concentrate
This is the cheapest and most common way.
It is produced by ultrafiltration of whey and normally offers protein concentrations between 70 and 80%, thus also containing some carbohydrates (lactose) and fats.
Since the concentration of this protein is around 70-80%, it means that for every 100g we have on average between 70 and 80 grams of pure protein, which is a very good value.
Furthermore, it has a high amount of BCAA's and other essential amino acids and is quickly absorbed.
Whey Protein Isolate
The isolated form is basically an evolution of the concentrated version.
It can be produced through various filtration techniques and achieves protein values in the range of 85-95%, which is excellent.
Furthermore, due to greater filtration, the fat and carbohydrate values are greatly reduced, reaching zero, eliminating lactose.
For example, in a protein with 95% concentration, we have 95g of high quality protein per 100g.
Hydrolyzed Whey Protein
This is the latest production technique for this type of supplement.
It is produced through the enzymatic hydrolysis of concentrated and/or isolated Whey.
With this technique the protein is absorbed more quickly, as the peptide bonds are separated and digestion is facilitated.
This is normally the most expensive way.
What are the benefits of Whey Protein?
Protein is an essential macronutrient and plays a crucial role in muscle development and maintenance, as well as many other physiological processes.
Simply put, amino acids are the building blocks that make up proteins and proteins are the building blocks that make up muscles.
Furthermore, amino acids play an important role in maintaining a healthy immune system, cardiovascular function and brain metabolism.
Supplementing with protein brings many benefits, which essentially come from the biological function of essential amino acids.
Whey protein is a complete protein, with a high amount of L-Leucine, essential for stimulating protein synthesis, among other EAA's.
Some of the reasons for using this type of supplement:
- Stimulates protein synthesis(3)(6)
- It is quickly absorbed/digested
- It is easy and convenient to use
- Increases the anabolic response to resistance training(3)(2)
- May function as an anti-catabolic during prolonged aerobic activities(2)
- Strengthens the immune system(5)
- Promotes fat loss(4)
- Helps maintain lean mass(3)(4)
- Help with recovery (1)(2)
How does it compare to other types of protein?
The most popular way to determine the quality of a protein is through biological value.
The biological value of a protein refers to a practical measure that assesses the degree to which it is possible for us to utilize that protein.
Basically, the higher the biological value of a protein, the more effective it will be used.
- Concentrated and isolated whey - Between 100 and 159
- Full egg? 100
- Milk ? 91
- Egg white ? 88
- Cottage cheese ? 84
- Tuna ? 83
- Chicken ? 79
- Peanuts? 68
- Oat ? 58
How and when to take Whey Protein?
The best time to take this supplement is undoubtedly before and after training, however, it can be used throughout the day when you want a quality source of protein.
Example: Add protein to your snack.
There is no universal value for the amount to take per day, as this always depends from person to person and should be used as a way to reach daily protein requirements.
An article that addresses this topic in more detail is The best times to take Whey.
What are the side effects of Whey Protein?
This supplement is normally well tolerated, however, in special cases the following may occur:
- Bloating/intestinal discomfort
- Nausea
- Gases
- Allergic reactions
These problems normally arise when there is a food allergy (lactose) or when protein consumption is too high.
If you experience intestinal discomfort with concentrated whey, try an isolate or a whey supplement with added digestive enzymes to facilitate digestion.
How to choose a good Whey Protein supplement?
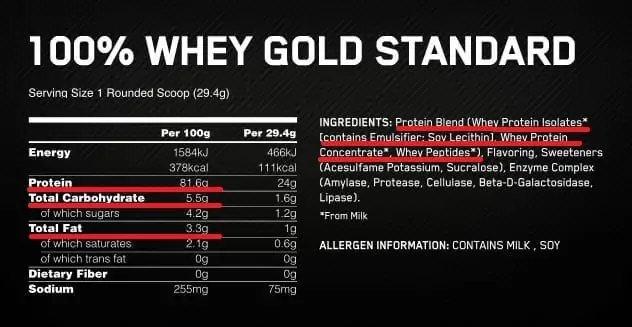
To choose a good Whey Protein supplement, the first step is always to look at the product label, analyzing the ingredients and nutritional value.
The supplement must have at least between 70 and 80% of protein, that is, between 70g and 80g of protein per 100g, ideally being around 80% in the case of concentrate and 90% in the case of isolate.
If it is a mixture of several proteins, it should contain between 75% and 85% of protein.
Protein sources should always be concentrated, isolated or hydrolyzed Whey.
You can have just one of them or a mix, depending on what you are buying.
Another important point is to analyze the additions made by the brand and the aminogram.
If you see additions such as glycine or taurine on the label, it is usually a bad product.
In the aminogram you should also look at the amounts of BCAA's (Leucine, isoleucine and valine).
A good Whey Protein contains at least between 17g and 18g of BCAA's in the case of concentrate, and 20-22g in the case of isolate.
Furthermore, a good Whey Protein has low amounts of carbohydrates (5-10g/100g) and fats (4-8g/100g).
Here you have our list of best whey protein supplements from the market.
Does Whey make you fat? Does Whey lose weight?
To gain weight you need to have a caloric surplus, that is, to eat more calories per day than you consume, so it doesn't just depend on Whey.
A Whey protein shake has around 100 calories, making it very difficult for anyone to gain weight through these shakes.
For this to eventually happen, your diet would have to already be very high in calories, and the Whey would have increased even more, even so it wouldn't make a very significant contribution to weight gain.
That said, using Whey Protein to gain muscle mass is a good idea, as it will help increase the protein content of your diet and its quality.
For those looking to lose weight, this supplement can be a good ally in maintaining lean mass while eliminating fat.
What is the best Whey Protein supplement?
The best supplement is the one that has the highest amount of quality protein, with the lowest amount of carbohydrates and fats.
You find here our Top 10 Whey supplements.
What is the worst Whey Protein supplement?
Products with a high amount of carbohydrates and low amounts of protein should be avoided.
Protein sources should be whey protein and not wheat and other proteins.
Techniques such as aminospiking are also not welcome. (See 100% Whey Prime review).
Concentrated Whey or Isolated Whey?
Whey Concentrate is the most economical whey supplement and is generally well tolerated.
Depending on the concentration of the powder, it is a excellent option for those who don't want to spend a lot of money and have a quality protein supplement.
As for disadvantages, it has a slightly lower bioavailability compared to the isolate and a lower protein concentration.
It also has a little lactose and if you are intolerant it is not a good idea.
As for Whey Isolate, it has a very high bioavailability, is even easier to digest, is very low in fats/carbohydrates and has a very high protein concentration (+90%).
The downside?
The price.
You can find our article here Isolated vs Concentrated Whey, is the isolated one worth it?
Conclusion
Whey Protein supplementation is very famous, and for obvious reasons.
It is an economical source of protein, with an excellent amino acid profile and is very practical, making it much easier to reach the necessary daily protein values.
Although it doesn't work miracles, its benefits are evident, and if you're looking for your first supplement, a good Whey Protein is probably the best bet.
Pass here in this article where we show you the best Whey protein supplements or take a look at our analytics to make sure you are buying a good product.
If you have any questions, use the comments area below.
References
(1) https://jissn.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1550-2783-5-S1-P6 (two) https://europepmc.org/article/med/20048505 (3) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23343671/ (4) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18371214/ (5) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25530736/ (6) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24257722/
Should I use whey protein on non-training days?
It just depends on your diet
If you can reach your daily protein values without using Whey Protein, you do not necessarily need to use this supplement on non-training days.
If you are unable to reach the required daily protein, you can use it to achieve this even on days when you don't train.
Do I use water or milk to mix my smoothie?
You can use both water and milk, however, before and after training it is ideal to use water as milk will delay the digestion of the protein.
Furthermore, don't forget that milk has a significant amount of sugar and some fat.
I'm lactose intolerant, can I use Whey Protein?
Yes, however you should use isolated whey as its lactose content is very low or zero.







Congratulations on the guide, it's really very enlightening :)
Keep going!
Excellent guide!
I'm loving this site for answering my questions about Whey protein. But I would like to know how daily needs vary depending on a person’s activity, weight and goals…
Weight gain/muscle mass: https://ginasiovirtual.mystagingwebsite.com/quantas-calorias-utilizar-para-ganhar-massa-muscular/
Weight/fat loss: https://ginasiovirtual.mystagingwebsite.com/quantas-calorias-ingerir-para-perder-peso/